Learning Modules
Module 03
Common Q & A
01. Role of the vaccines
(1) Why should I have the COVID-19 vaccine?
The COVID-19 vaccine is effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalisation and death. Some evidence showed that the vaccine can reduce the chance of transmission of the virus, which also means that get vaccinated help protect those people around you. Local studies have shown that three doses of Sinovac or BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines are effective in preventing risk of severe illness and death [2].
(2) Why should I have the pneumococcal vaccine?
Pneumococcal infections are usually treated with antibiotics, however, the organisms causing the infections are becoming more resistant to antibiotics. Therefore, prevention of a pneumococcal infection is more important than treatment. Vaccination against pneumococcal infection is one of the most effective ways to prevent the disease [3].
(3) Why should I get an influenza vaccine?
Influenza vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent seasonal influenza and its complications, as well as to reduce hospital admissions and deaths due to influenza. The influenza vaccine is effective in preventing influenza and its complications, therefore, all members of the public, except those with known contraindications to the vaccine, should receive the seasonal influenza vaccine annually to protect their health [4].
(4) Why is it necessary for older adults to receive COVID-19, influenza and pneumococcal vaccines for early protection?
- Older adults and persons with chronic diseases are at higher risk of severe illness and death. Sinovac and BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines are highly effective in reducing the risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 [5].
- In addition, secondary bacterial pneumonia is an important cause of morbidity and mortality for those infected with influenza [3]. Inactivated influenza vaccines provide moderate protection against influenza in older adults. Available research data have shown that recombinant influenza (flu) vaccines may be more effective than standard dose inactivated influenza vaccines in older adults. Data from a local study have also shown that concomitant administration of influenza and pneumococcal vaccines reduce hospital admissions and mortality in older adults [4].
02. Pre-vaccination information
(5) What are the age limits for vaccination against the three common preventable infectious respiratory diseases?
- The minimum age for receiving the Sinovac vaccines was lowered to 6 months of age on 4 August 2022. The minimum age for receiving the BioNTech vaccines was lowered to 6 months of age on 9 November 2022 [5].
- Persons aged 6 months and above (i.e., including infants) are recommended to receive influenza vaccination [4].
- Children aged under 2 years are recommended to receive pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV) under the Hong Kong Childhood Immunization Programme. These consist of two primary doses of PCV vaccines at 2 and 4 months of age and one booster dose at 12 months of age [3].
(6) Who should not receive COVID-19 vaccines?
People who have had a severe allergic reaction to the previous dose of the same vaccines, the active substance or any components of the vaccines should not be vaccinated [5].
(7) Who should not receive pneumococcal vaccines?
People who experienced a severe allergic reaction following a prior dose of pneumococcal vaccine or to the vaccine component or any diphtheria toxoid-containing vaccine should not receive further doses of pneumococcal vaccines [3].
(8) Can I get the pneumococcal vaccine together with COVID-19 and Influenza vaccines?
Inactivated influenza vaccines can be co-administered with, or received at any time before or after injections of other inactivated vaccines (e.g., Sinovac COVID-19 vaccine) or live-attenuated vaccines (e.g., live-attenuated influenza vaccines). An inactivated influenza vaccine if given together with other vaccines, each vaccine should be administered at a different injection site [4].
(9) What are the differences between 23-valent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine (23vPPV) and 3-valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13)?
PCV13 is effective in preventing invasive pneumococcal diseases and non-invasive pneumonia caused by pneumococcus. Clinical studies have shown that 23vPPV is effective in preventing invasive pneumococcal diseases but less effective in preventing non-invasive pneumonia caused by pneumococcus. It is worth noting that 23vPPV contains more serotypes of pneumococcus, which theoretically provides people additional protection [3].
03. Arrangements for vaccination
(10) People who have had COVID-19 need to be vaccinated?
Yes. The level of protection obtained after infecting COVID-19 virus varies from person to person. A higher level of immunity can be achieved with timely vaccination [5].
(11) Can I be vaccinated during menstruation, pre-pregnancy, pregnancy and breastfeeding?
- The vaccines can be administered during menstruation [1].
- There is no evidence showing that the vaccines affect fertility.If you plan to be pregnant, you should administer the vaccines [1].
- Women during pregnancy and breastfeeding can receive BioNTech and Sinovac vaccines. The risk of severe illness caused by the novel coronavirus is higher during pregnancy [2]. Some studies have shown that COVID-19 vaccination can reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in pregnant women [5]. The antibodies produced by the vaccines can be transferred from pregnant women to their fetuses through the umbilical cord. Women who are breastfeeding can also give protection to their babies [5].
(12) If I have received the flu vaccines, can I still receive COVID-19 vaccines?
Yes. There is no conflict between the two [1].
(13) Can I receive a second dose if I have a serious adverse reaction after administering the first dose of COVID-19 vaccines?
- If a person has a serious adverse reaction after administering the first dose of the vaccines and needs to be admitted to hospital for treatment, he/she should consult a doctor after recovery before receiving the second dose [2].
- If you experience serious adverse reactions and require hospitalization after administering the first dose of the vaccine, the Department of Health will cancel your appointment for the second dose through the government's online vaccine appointment system. This is to allow you to consult with a doctor before rescheduling the appointment for the second dose of the vaccine, ensuring that you receive appropriate medical advice and supervision [2].
(14) Can I choose a vaccine different from the first dose for the second or third dose?
Yes. Receiving a different COVID-19 vaccine for the second or third doses is safe and effective [1].
(15) After the first dose of COVID-19 vaccines, can I receive the second dose at an interval longer than the recommended?
People are advised to follow the recommended interval as far as possible. You should receive the second dose of vaccines as soon as possible if the recommended interval has elapsed since the first dose of vaccines was administered [2].
(16) What is the interval between COVID-19 vaccines and other vaccines?
With informed consent, COVID-19 vaccines can be administered at the same time with other vaccines (including live attenuated vaccines), or at any time before or after administering other vaccines. If a person wants to receive COVID-19 vaccines and the live attenuated vaccines (e.g., measles, mumps, rubella and varicella combination vaccines; live attenuated nasal spray influenza vaccines) at separate times, an interval of 14 days between the two vaccines is sufficient [1].
(17) How many doses of COVID-19 vaccines are required?
- Immunity and clinical protection levels fall with increasing time, therefore, the World Health Organization recommends an additional dose of COVID-19 vaccines (a booster dose) for groups that have completed their initial immunization (currently one, two or three doses of COVID-19 vaccines, depending on the types of the vaccines and the populations being vaccinated) [1].
- According to the vaccination schedule of the Department of Health, the general public and immunocompromised persons aged 18-49 can opt for the fourth or fifth doses of COVID-19 vaccines, while the fourth dose is recommended for immunocompromised persons [2, 6].
- For persons aged 50 or above, the fourth dose of Sinovac or BioNTech is recommended for both the general public and immunocompromised persons; the fifth dose is optional for the general public and the immunocompromised persons [6].
- Please note that immunocompromised individuals are required to receive three doses of the original strain of vaccines before they can opt for the fourth dose of BioNTech bivalent vaccines [6].
For details of the fourth or fifth doses of vaccination, please refer to the following table:
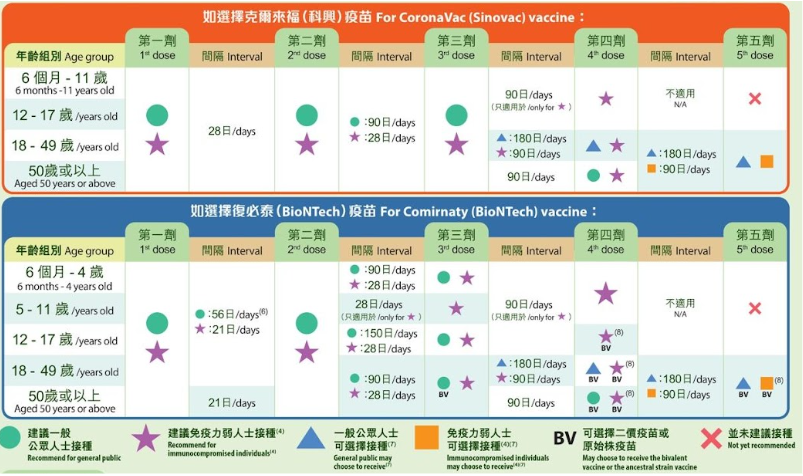
Source: Centre for Health Protection [6]
Local data in Hong Kong show that three doses of COVID-19 vaccines (i.e., Sinovac and BioNTech vaccines) are highly effective in reducing hospitalization and mortality after an infection in adults of all ages [5]. The Government will update information on the vaccination programme from time to time. Please pay attention to the Government's announcements and visit the website of COVID-19 Vaccination Programme.
(18) What are the recommendations on the use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine?
- The Scientific Committee on Vaccine Preventable Diseases (the Scientific Committee) recommends high-risk individuals aged 2 years or above, receive a single dose of PCV13, followed by a single dose of 23vPPV 1 year later. For those who have already received 23vPPV, a single dose of PCV13 should be administered 1 year after previous 23vPPV vaccination. For those who have already received PCV13, a single dose of 23vPPV should be administered 1 year after previous PCV13.
- The Scientific Committee recommends children aged below 2 years to receive pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV) under the Hong Kong Childhood Immunization Programme (HKCIP). These include two primary doses given at 2 and 4 months of age, followed by a booster dose at 12 months of age.
- For older adults aged 65 years or older without high risk health condition, the Scientific Committee recommends either a single dose of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) or a single dose of 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (23vPPV) [3].
(19) When is the best time to get a flu shot?
It is recommended to receive the vaccine before the winter flu season. The reason is to allow sufficient time for the body to build up its immunity against the influenza virus, which usually takes 2 weeks [4].
(20) Where can I get vaccinated against the three common infectious respiratory diseases?
| COVID-19 vaccines | Influenza vaccines | Pneumococcal vaccines | |
| Vaccination venues | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Charges |
Free additional boosters are given to the following eligible persons [7]:
Non-eligible persons are required to pay for the booster at their own expense. The fee ranges from $1,000 to $2,000. For details, please click here to view the government leaflet. |
|
|
04. Safety and efficacy of the vaccines
(21) Are the vaccines safe enough? Do they contain toxic ingredients?
They are safe enough.
| COVID-19 vaccines | Influenza vaccine | Pneumococcal vaccine |
| The vaccines contain different components for maintaining its safety and efficacy. Each component was tested and certified as safe during the manufacturing process [5]. | Inactivated influenza vaccines are very safe and generally have no side effects except for possible soreness, redness and swelling at the injection [4]. | The pneumococcal conjugate vaccines have been proven safe [3]. |
(22) Do COVID-19 vaccines protect you from different variants of the virus?
Studies have shown that existing vaccines are effective in protecting people from non-variant strains. The efficacy of the vaccines in protecting individuals from different variants vary from one vaccine to another [5].
(23) Can I trace the batch/lot numbers of the vaccines that I have received?
Yes. The vaccines batch/lot numbers can be found in the vaccination records [5].
(24) How long will COVID-19 vaccine protection last?
Current data indicate that the vaccines are effective for at least 6 months in most people for protecting them from severe illness and death [1]. The approved COVID-19 vaccines provide a good level of protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death. When the opportunity for a booster dose arises, it should be administered to enhance protection against severe illness and death caused by COVID-19. This is especially important for older adults, individuals with underlying health conditions, or those with increased exposure to the virus, as they may experience a faster decline in immunity. Therefore, it is important to ensure that high-risk groups adhere to the recommended vaccination schedule for them [10].
(25) What is the protective efficacy of an influenza vaccine?
Currently, vaccination is the most effective way to prevent influenza. Generally speaking, the protective efficacy of an influenza vaccine is about 70-90%. For older adults, it can reduce the severity and complications of influenza by 50-60%, as well as the mortality rate by 80% [11].
05. What you need to know after the vaccination
(26) Do side effects prove that the vaccines are effective?
No. The vaccines stimulate the body's immune system and protect the body from viral infections, which is a process that sometimes causes side effects, but not all of the people who have received the vaccines experience the side effects [1]. Common adverse reactions after receiving vaccines include mild pain and swelling at the site of the injection for a short period of time. Most of these reactions subside spontaneously within two days. Some people may experience mild fatigue, fever, headache, muscle pain or chills. It is very rare to experience severe pain at the needle site or difficulty in moving the arm. Severe pain at the injection site or difficulty in moving the arm being injected is very rare[3].
(27) Is it safe to take antibiotics after the vaccination?
Yes. There is no association between the two [1].
(28) Can I drink alcohol after the vaccination?
No. It is not recommended. Although alcohol does not have any effect on the safety or efficacy of the vaccines, drinking alcohol may worsen the normal mild to moderate side effects that occur after the vaccination [1].
(29) What should be noted after receiving the vaccine?
To prevent the flu, vaccinated individuals should maintain good personal and environmental hygiene habits, pay attention to balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, get adequate rest, and avoid smoking [11].
(30) What can I do if I still have some questions about the Vaccination Programme?
You can call the HKSAR Government hotline at 3142 2366 or go to the HKSAR Government's website forCOVID-19, Flu, Pneumococcal and the website of the World Health Organization for COVID-19, Flu and Pneumococcal.



